Datacenter power failures put lives at risk when employees can’t find safe exits in the dark. Federal regulations mandate specific egress lighting standards that many facility managers overlook.
We at PacLights see compliance gaps that expose organizations to serious liability. This guide covers the essential requirements every datacenter manager needs to implement.
What Are the Core Egress Lighting Standards
NFPA 101 Life Safety Code Sets Non-Negotiable Requirements
NFPA 101 Life Safety Code establishes the baseline for datacenter emergency lighting with specific requirements that leave no room for interpretation. Datacenters must maintain minimum 1.0 foot-candle illumination along all egress paths during normal operations, then drop to an average of 0.6 foot-candles under emergency power. The maximum-to-minimum illumination ratio cannot exceed 40:1, which prevents dangerous shadows that could cause falls during evacuations. Emergency systems must activate within 10 seconds of power loss and operate for 90 minutes minimum.

Monthly 30-second functional tests and annual 90-minute duration tests are mandatory, with detailed logs required for compliance audits.
OSHA Standards Override Local Building Codes
OSHA standards 1910.37 and 1910.38 supersede local building codes in most situations and require emergency lighting in all occupied datacenter areas (server rooms, UPS areas, and generator spaces). The International Building Code mandates 1 foot-candle minimum illumination but allows reduction to 0.06 foot-candles after 90 minutes under emergency power. Local authorities can impose stricter requirements, which makes code research essential before installation. Non-compliance results in regulatory fines that average $15,000 per violation according to OSHA enforcement data.
Documentation Failures Account for Most Violations
Documentation failures account for 60% of emergency lighting violations during inspections, which makes record-keeping systems critical for facility managers. UL 924 compliance requires self-diagnostic capabilities in modern emergency lighting systems that automatically log test results and battery status. Facilities must maintain written logs that document monthly tests, annual duration tests, and all maintenance activities for minimum three years.
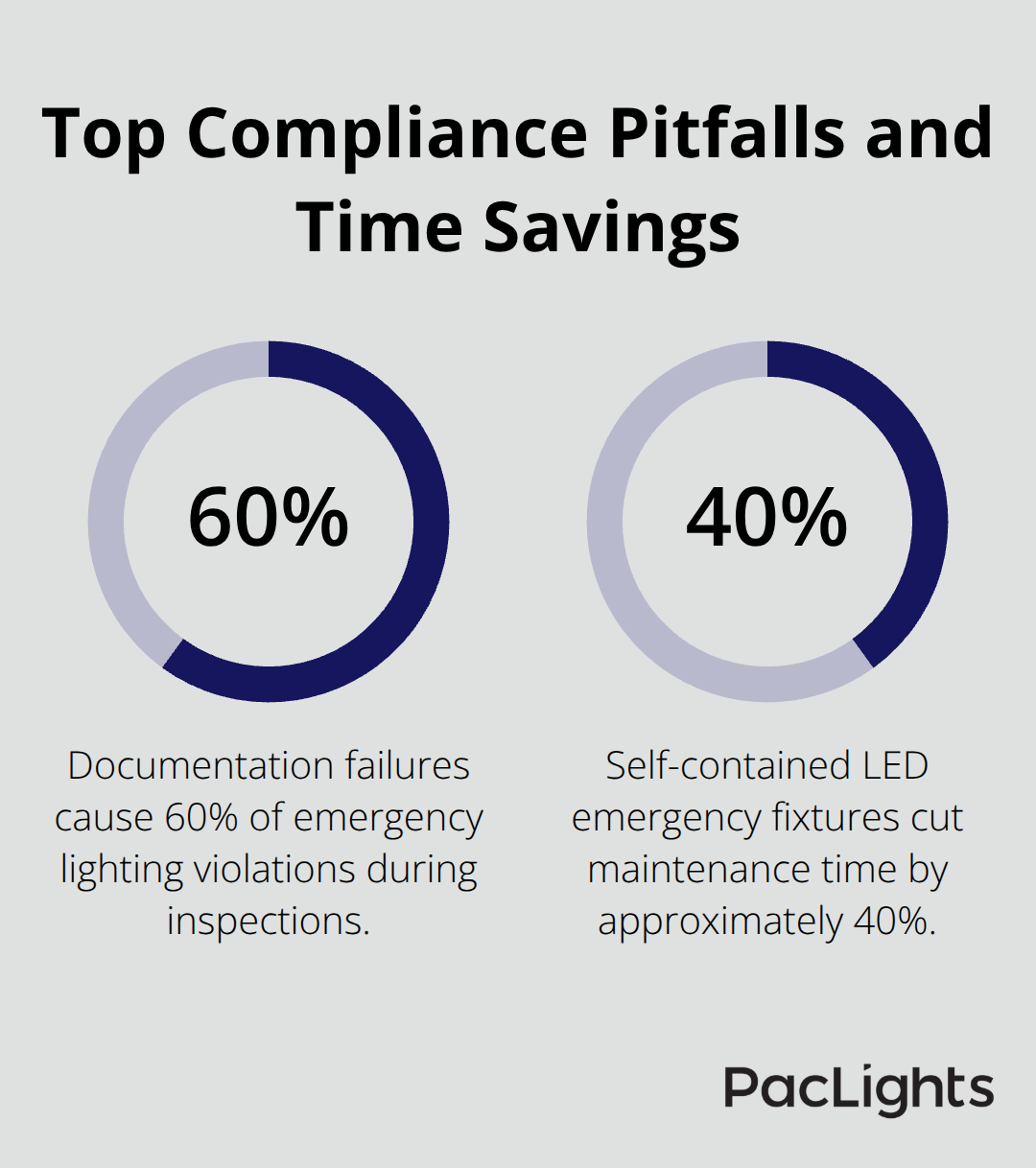
Self-contained LED emergency fixtures reduce testing complexity compared to central inverter systems and cut maintenance time by approximately 40% based on facility management studies.
Test Switch Access Simplifies Compliance Verification
Test switches must remain accessible in UPS rooms and generator areas to facilitate compliance testing without operations disruption. These switches allow facility managers to verify emergency lighting function during scheduled maintenance windows rather than wait for actual power failures. Proper switch placement reduces testing time and helps maintain consistent compliance records that inspectors expect to review.
The next step involves understanding how these standards translate into specific hardware requirements and system components that datacenters need to implement.
What Hardware Components Make Emergency Lighting Systems Work
Emergency Exit Signs Require Specific Illumination Standards
Emergency exit signs must deliver 54 lux illumination on sign faces with LED panels that maintain visibility through smoke and dust conditions common in datacenters. These signs use photoluminescent materials as backup when electric power fails completely. Self-contained emergency units integrate battery backup directly into each fixture, which eliminates single points of failure that plague centralized systems. The SeamLine Batten connects to centralized backup systems while it maintains UL 924 compliance for emergency applications.
Fixture Placement Determines Coverage Effectiveness
Wall-mounted emergency lights work best in narrow corridors between server racks where space constraints limit ceiling options. Ceiling-mounted fixtures provide broader coverage in cold aisles and main pathways where personnel move during evacuations. IP65-rated fixtures resist condensation and particulate ingress that can compromise performance in datacenter environments. Strategic placement avoids shadows and provides consistent illumination along egress routes without obstruction from cable trays or HVAC equipment.
Battery Systems Must Handle 90-Minute Runtime Requirements
Nickel-metal hydride batteries outperform sealed lead-acid options in datacenter environments because they tolerate temperature fluctuations better and last 7-10 years versus 3-5 years for lead-acid. Central inverter systems can power multiple fixtures from a single battery bank, but self-diagnostic LED units reduce maintenance complexity by 40% according to facility management studies. Each battery system must undergo monthly 30-second tests and annual 90-minute duration tests with automatic capabilities that generate compliance reports. Modern systems include battery status alerts that notify facility managers 60 days before replacement becomes necessary.
Fire Alarm Integration Prevents System Conflicts
Emergency systems must integrate with fire alarm systems to prevent conflicts between evacuation routes and fire suppression systems that could create confusion during emergencies. Management systems should monitor emergency status continuously and generate alerts when fixtures fail or batteries drop below 80% capacity. Integration allows facility managers to test emergency systems remotely during scheduled maintenance windows rather than manually activate each fixture. This coordination also synchronizes visual and auditory alarms with circuits to enhance emergency response effectiveness.
Proper installation requires more than just hardware selection – strategic placement and maintenance protocols determine whether these systems actually protect personnel when power fails.
How Do You Install Emergency Lighting That Actually Works
Mount Fixtures Where People Actually Walk
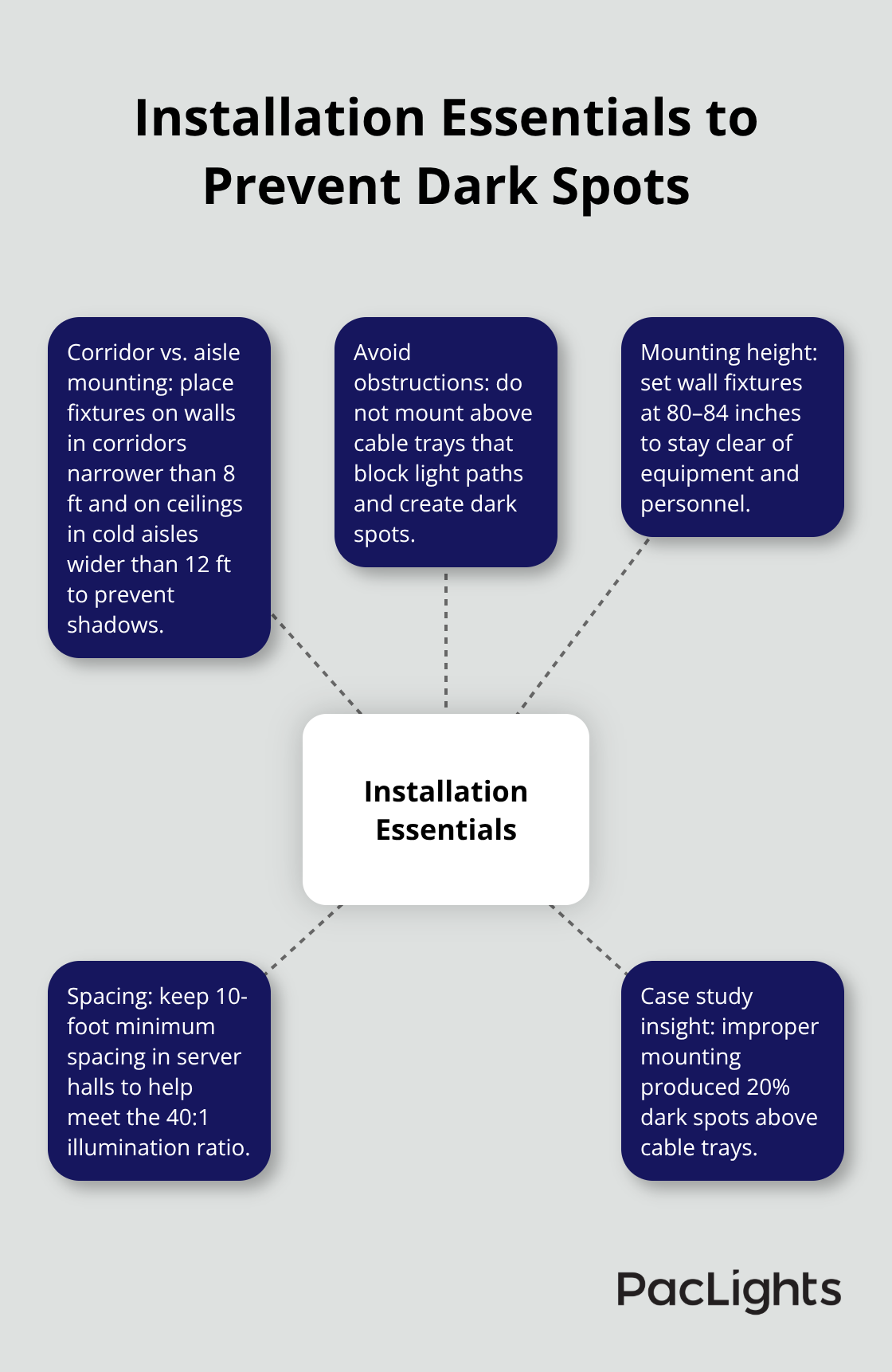
Emergency fixtures must go on walls in corridors narrower than 8 feet and on ceilings in cold aisles wider than 12 feet to eliminate shadows that cause falls during evacuations. The Malaysian colocation facility case study showed that 20% of dark spots occurred when fixtures were mounted incorrectly above cable trays that blocked light paths. Mount wall fixtures at 80-84 inches height to prevent obstruction by equipment racks and personnel. Ceiling fixtures need 10-foot minimum spacing in server halls to maintain the 40:1 maximum-to-minimum illumination ratio required by NFPA 101.
Position Test Switches for Easy Access
Install test switches within 6 feet of fixture locations in UPS rooms and generator areas to enable monthly tests without operations disruption. These switches allow facility managers to verify emergency functions during scheduled maintenance windows rather than wait for actual power failures. Proper switch placement reduces test time and helps maintain consistent compliance records that inspectors expect to review during audits.
Execute Monthly Tests or Face Violations
Monthly 30-second functional tests and annual 90-minute duration tests are mandatory with written documentation required for minimum three years according to UL 924 standards. Self-diagnostic LED fixtures automatically generate test reports that reduce compliance time by 40% compared to manual procedures. Schedule quarterly lux measurements with calibrated meters to verify 500+ lux levels in data halls and 54 lux minimum on exit signs. Weekly walk-throughs identify flickering LEDs and dust accumulation that compromise performance before they cause compliance failures.
Document Every Test and Maintenance Activity
Document every test result, battery replacement, and maintenance activity in logbooks that inspectors review during audits. Facilities that implement preventive maintenance frameworks (weekly, monthly, and quarterly tasks) reduce emergency failures by 60% and avoid the average $15,000 per violation fines that OSHA enforcement data shows. Keep detailed records for minimum three years to demonstrate compliance with federal regulations and protect against liability claims.
Final Thoughts
Emergency egress lighting compliance protects datacenter personnel and prevents costly violations that average $15,000 per incident. NFPA 101 mandates 1.0 foot-candle minimum illumination with 90-minute battery backup, while OSHA standards 1910.37 and 1910.38 require emergency systems in all occupied areas. Monthly 30-second tests and annual 90-minute duration tests with proper documentation prevent the 60% of violations that record-keeping failures cause.
Self-diagnostic LED fixtures reduce maintenance complexity by 40% compared to centralized systems and automatically generate compliance reports. Strategic placement eliminates shadows while IP65-rated fixtures withstand datacenter environmental conditions. The Malaysian facility case study demonstrated how proper fixture selection reduced maintenance calls by half after operators switched from fluorescent systems.
Implementation starts with code research, then moves to fixture selection based on space constraints and environmental factors. We at PacLights provide LED lighting solutions that meet regulatory requirements for datacenter applications. Facility managers who implement preventive maintenance frameworks reduce emergency failures by 60% and maintain consistent compliance records that protect against liability exposure during inspections.


Disclaimer: PacLights is not responsible for any actions taken based on the suggestions and information provided in this article, and readers should consult local building and electrical codes for proper guidance.